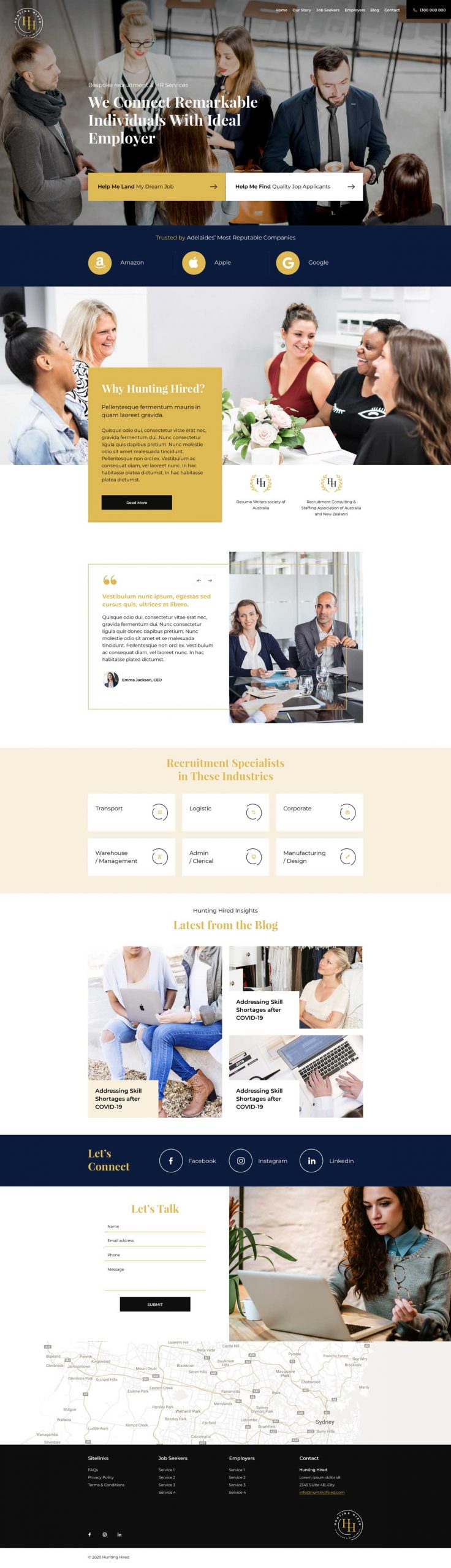
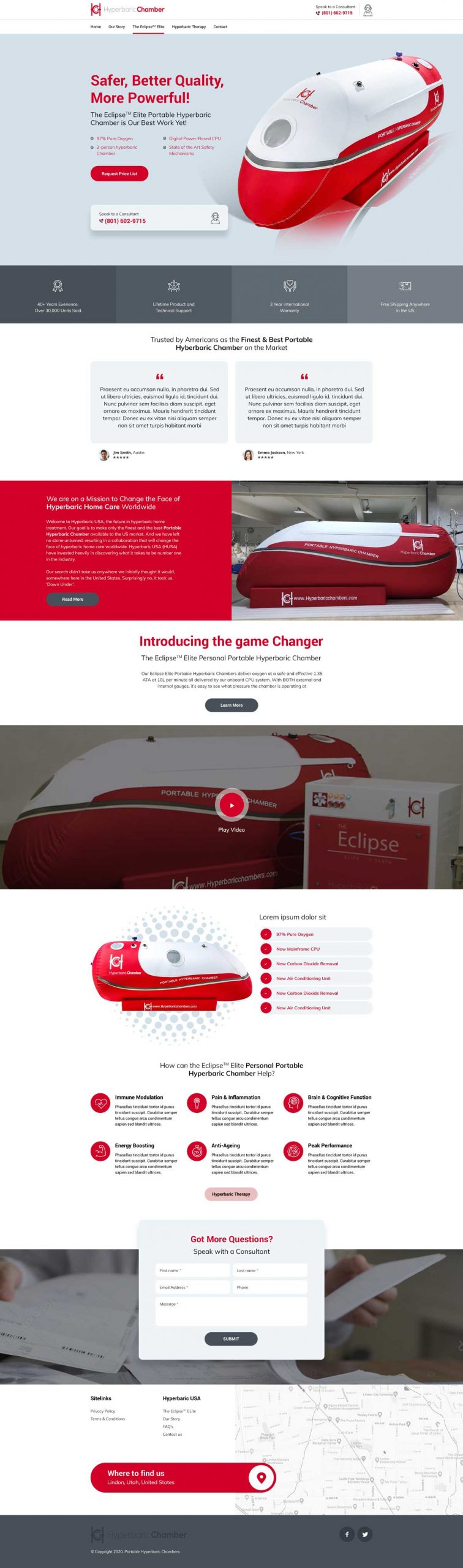
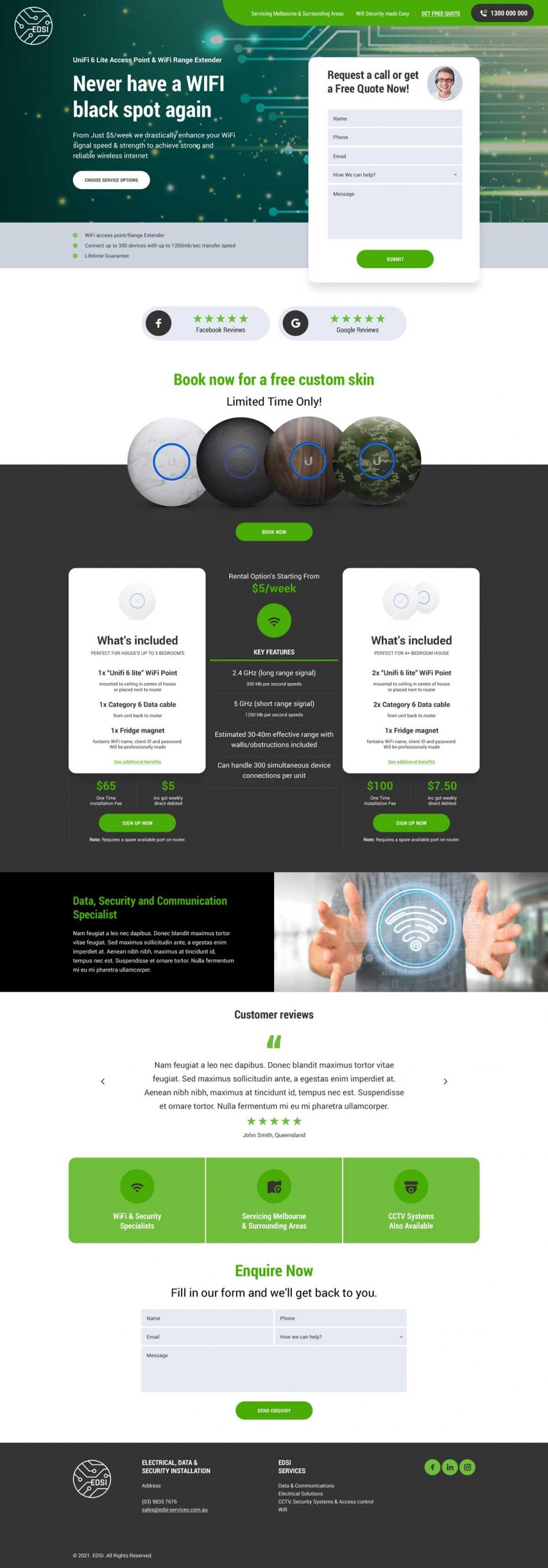
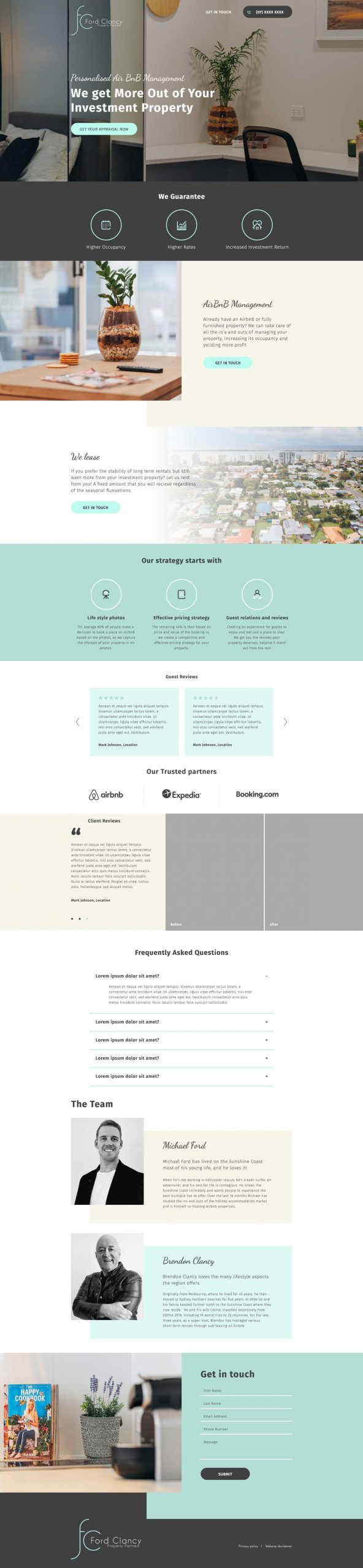
Web Design Services
High Quality Websites That Generate More Leads, Calls & Sales
We are a local team with 14 years of combined experience. And you get premium support with us.












How We Can Help


WEBSITE DESIGN
We can design & develop a brand new website on the most suitable platform to match your business objectives.


WEBSITE DEVELOPMENT
We can develop a new feature/functionality on your website or eCommerce store.
WEBSITE SUPPORT & MAINTENANCE
We can investigate bugs & fix website errors. We can also perform regular security audits & updates to keep your website safe & functional & performant.


SYSTEM INTEGRATIONS
We can develop integrations between your website and a range of software solutions.
Why work with us?
You get a website that stands out, converts and... grows your business!
You'll collaborate with a team of marketers strategiest, designers and developers - we understand the full picture of what makes websites work. We'll design & build a website you love, your customers love and makes you loads of money.
You get access to the best, smartest and most innovative people in the industry.
Our team is awesome! We dare to dream beyond what's deemed possible and as a results deliver state-of-the-art, cutting edge web design & development solutions.
You get a website that's easy to manage, update and operate.
We believe in simplicity. Our user friendly platform allows you to easily update words, images & keep things up to date. And... if you ever need help, we're just a phone call away.
You get a local team who supports Australian business.
You get one-on-one access to our team to discuss your ideas and plans. While this isn't as cheap as outsourcing overseas... you'll actually end up with the website you envisioned and enjoy the process of building it with our team. We have offices in Brisbane, Sunshine Coast & Gold Coast.
You get a mobile, tablet & cross device ready website Google will love!
Your customers want to find & interact with your business in different ways, platforms & devices. We are experts at figuring out what that looks like for you and create your website accordingly. We make sure your site engages visitors and displays your message correctly; whatever the device.
You get industry leading support.
We don't just build sites and leave you to figure things out. Our client relationships span 10 even 15 years. You become part of the Websites That Sell family and with that a full support team on a mission to generate results for you.
Trusted By Local & National Brands


















Heres some of our work




We spent a lot of money on another advertising company who didn't know what they were doing.
When the Websites That Sell team redesigned the site, and I saw it, I almost fell off my chair. It was a huge change, and they definitely knew what they were doing. It was a 20 times better result than our previous site.
Another thing we noticed about the team, which is very refreshing, is that they are very prompt with email correspondence. They always replied immediately and made the changes we needed as quickly as possible. Changes were done pretty much in a flash.
Thanks for your work.






Awesome, awesome, you are fantastic and unbelievable. In my 10 years of business, you have surpassed all others before you regarding your service. You have made my day.
In my business, I go beyond for my clients, and sometimes I question myself for the heart, soul and effort I put in and feel that I can be taken advantage of. But today, karma came to me.
Like you, I will continue giving my all as I do it for selfless reasons, and if people take advantage of that, that's their issue, not mine. Thank you again. Keep well and happy.


Our proven process that delivers excellence








Case Studies
real companies, real results!
Want to work with us?
Our vision is to be the first & last digital marketing agency Aussie business owners will ever need. Because we live and die by results.
